Systems manager: Systems Manager: 7 Powerful Roles and Responsibilities Revealed
If you’ve ever wondered who keeps the digital heartbeat of a company strong, look no further than the systems manager. This pivotal role blends technical mastery with leadership finesse to ensure seamless operations across IT infrastructures.
What Is a Systems Manager?

A systems manager is a key figure in any organization that relies on technology to function. They oversee the planning, implementation, and maintenance of computer systems, ensuring that both hardware and software components operate efficiently and securely. Their role bridges the gap between technical teams and business objectives, making them indispensable in today’s digital-first environment.
Core Definition and Scope
The term systems manager refers to a professional responsible for managing an organization’s IT systems. This includes servers, networks, databases, operating systems, and cloud platforms. Their scope isn’t limited to fixing issues—it extends to strategic planning, system optimization, and future-proofing technology investments.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Responsible for system uptime, performance, and security
- Acts as a liaison between IT staff and executive leadership
- Ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment for computer and information systems managers is projected to grow 16% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Evolution of the Role
The role of a systems manager has evolved significantly over the past few decades. In the 1980s and 1990s, it was primarily focused on mainframe administration and local network oversight. Today, with the rise of cloud computing, cybersecurity threats, and remote work, the systems manager must be agile, forward-thinking, and well-versed in emerging technologies.
- From on-premise servers to hybrid cloud environments
- Increased focus on data governance and regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
- Greater integration with DevOps and agile development practices
“The modern systems manager isn’t just a technician—they’re a strategic enabler of business growth.” — TechLeaders Forum, 2023
Key Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
The day-to-day duties of a systems manager are diverse and demanding. They must balance technical troubleshooting with long-term planning, team leadership, and budget oversight. Let’s break down the core responsibilities that define this critical role.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Infrastructure Planning and Deployment
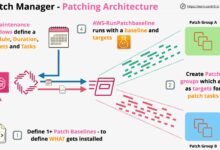
One of the primary functions of a systems manager is designing and deploying IT infrastructure. This involves selecting appropriate hardware and software, configuring networks, and ensuring scalability for future growth.
- Conducting needs assessments before new system rollouts
- Overseeing the installation of servers, storage solutions, and networking equipment
- Integrating new systems with existing platforms to avoid silos
For example, when a company migrates from on-site data centers to AWS or Microsoft Azure, the systems manager leads the transition, ensuring minimal downtime and maximum data integrity.
System Monitoring and Performance Optimization
A systems manager must continuously monitor system performance using tools like Nagios, SolarWinds, or Datadog. These platforms provide real-time insights into server health, network traffic, and application responsiveness.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Setting up alerts for CPU overload, memory leaks, or disk failures
- Conducting regular performance audits and tuning databases
- Implementing load balancing and failover mechanisms
Proactive monitoring allows systems managers to resolve issues before they impact users. This preventive approach can save companies thousands in lost productivity and revenue.
Security Management and Risk Mitigation
Cybersecurity is a top priority, and systems managers play a central role in protecting organizational assets. They implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption protocols, and access controls.
- Developing and enforcing security policies across departments
- Leading incident response during data breaches or ransomware attacks
- Conducting regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) emphasizes the importance of having dedicated personnel like systems managers to manage cyber risks effectively.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Essential Skills for a Successful Systems Manager
To excel as a systems manager, one must possess a unique blend of technical expertise, leadership ability, and business acumen. The most effective professionals in this role are not only skilled in IT but also understand how technology supports broader organizational goals.
Technical Proficiency
A deep understanding of operating systems (Windows, Linux, Unix), virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V), and cloud platforms (AWS, GCP, Azure) is essential. Systems managers must also be familiar with scripting languages like PowerShell, Bash, or Python to automate routine tasks.
- Mastery of network protocols (TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP)
- Experience with database management (SQL, NoSQL)
- Knowledge of containerization tools like Docker and Kubernetes
Staying updated through certifications such as CompTIA Server+, RHCE, or AWS Certified Solutions Architect enhances credibility and competence.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Leadership and Communication Skills
While technical skills are crucial, the ability to lead teams and communicate clearly is equally important. A systems manager often reports to C-level executives and must translate complex technical issues into business terms.
- Delegating tasks effectively among junior administrators
- Facilitating cross-departmental collaboration (e.g., with HR, finance, or marketing)
- Presenting IT budgets, project timelines, and risk assessments to stakeholders
Strong interpersonal skills help build trust and ensure smooth operations across departments.
Problem-Solving and Strategic Thinking
When a critical system goes down, the systems manager is expected to diagnose and resolve the issue quickly. This requires analytical thinking, calm under pressure, and a methodical approach to troubleshooting.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Using root cause analysis (RCA) to prevent recurring problems
- Anticipating future challenges based on usage trends
- Aligning IT strategy with business objectives like digital transformation or cost reduction
“The best systems managers don’t just fix problems—they prevent them.” — CIO Magazine, 2022
Systems Manager vs. IT Manager: Understanding the Difference
While the titles are sometimes used interchangeably, there are distinct differences between a systems manager and an IT manager. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify roles within an organization’s technology hierarchy.
Scope of Responsibility
A systems manager typically focuses on the technical aspects of IT infrastructure—servers, networks, operating systems, and performance tuning. In contrast, an IT manager has a broader scope, overseeing all IT operations including help desk support, software licensing, vendor management, and user training.
- Systems manager: deep technical focus on backend systems
- IT manager: broader administrative and operational oversight
- Both may report to a CIO or CTO, depending on company size
In smaller organizations, one person might wear both hats, but in larger enterprises, these roles are usually separated for efficiency.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Reporting Structure and Decision-Making
The systems manager often works under the IT manager or directly under the CIO. Their decisions are more technical in nature—such as choosing a new database platform or upgrading server capacity—while the IT manager makes higher-level decisions about staffing, budgets, and service delivery.
- Systems manager recommends technology upgrades based on performance data
- IT manager approves budgets and coordinates with procurement
- Collaboration between both roles ensures alignment between technical needs and financial constraints
For example, if a company plans to adopt AI-driven analytics, the systems manager evaluates the computational requirements, while the IT manager negotiates contracts with vendors.
How to Become a Systems Manager: Education and Career Path
Becoming a systems manager typically requires a combination of formal education, hands-on experience, and professional certifications. While paths can vary, there are common steps most successful professionals follow.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Educational Requirements
Most systems managers hold at least a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field. Coursework often includes networking, database management, cybersecurity, and systems architecture.
- Recommended degrees: B.S. in Computer Science, IT, or Management Information Systems (MIS)
- Advanced roles may require a master’s degree, especially in large corporations or government agencies
- Some enter the field via vocational training or military IT programs
Universities like MIT, Stanford, and Carnegie Mellon offer strong programs that prepare students for leadership roles in systems management.
Certifications That Boost Credibility
Professional certifications validate expertise and demonstrate commitment to ongoing learning. Employers often favor candidates with recognized credentials.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- CompTIA A+ and Network+: foundational knowledge
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate: cloud expertise
- CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional): security leadership
- ITIL Foundation: service management best practices
The International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC)² reports that CISSP holders earn 25% more on average than non-certified peers.
Typical Career Progression
Many systems managers start as IT support specialists or system administrators. With experience, they move into senior technical roles before transitioning into management.
- Entry-level: Help Desk Technician or Junior Admin (0–3 years)
- Mid-level: System Administrator or Network Engineer (3–7 years)
- Senior-level: Senior Systems Engineer or Lead Administrator (7–10 years)
- Management: Systems Manager or IT Operations Manager (10+ years)
Mentorship, internal promotions, and continuous skill development are key drivers of career advancement.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Tools and Technologies Used by Systems Managers
Modern systems managers rely on a wide array of tools to monitor, secure, and optimize IT environments. Mastery of these platforms is essential for maintaining high availability and performance.
Monitoring and Management Platforms
Tools like SolarWinds, Zabbix, and Datadog provide comprehensive visibility into system health. They allow systems managers to track metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and network latency in real time.
- Automated alerting for anomalies
- Dashboard customization for different teams
- Integration with ticketing systems like Jira or ServiceNow
These platforms reduce manual oversight and enable proactive maintenance.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Cloud and Virtualization Tools
With the shift to hybrid and multi-cloud environments, systems managers must be proficient in cloud orchestration and virtualization.
- AWS Management Console, Google Cloud Console, Azure Portal
- VMware vSphere for virtual machine management
- Terraform and Ansible for infrastructure-as-code (IaC)
Using IaC, systems managers can deploy entire server clusters with a single script, improving consistency and reducing human error.
Security and Compliance Tools
To protect sensitive data, systems managers use tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, endpoint protection platforms, and vulnerability scanners.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Splunk and IBM QRadar for log analysis and threat detection
- Nessus and OpenVAS for identifying system weaknesses
- BitLocker and LUKS for disk encryption
Regular audits using these tools ensure compliance with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI-DSS.
Challenges Faced by Systems Managers Today
Despite the rewards, the role of a systems manager comes with significant challenges. Rapid technological change, cybersecurity threats, and resource constraints make this a high-pressure position.
Keeping Up with Technological Change
The pace of innovation in IT is relentless. New frameworks, cloud services, and security protocols emerge constantly, requiring systems managers to engage in lifelong learning.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Demand for expertise in AI, machine learning, and edge computing
- Need to evaluate emerging technologies without disrupting current operations
- Pressure to adopt automation while managing legacy systems
According to a 2023 Gartner report, 60% of IT leaders say keeping up with tech trends is their biggest challenge.
Cybersecurity Threats and Data Protection
Ransomware, phishing, and zero-day exploits are growing in frequency and sophistication. Systems managers must remain vigilant to protect organizational data.
- Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and zero-trust architectures
- Training staff on social engineering risks
- Developing and testing disaster recovery plans
A single breach can cost millions in fines and reputational damage, making security a top priority.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Resource Limitations and Budget Constraints
Many systems managers operate under tight budgets and limited staffing. They must do more with less, often juggling multiple projects simultaneously.
- Justifying IT investments to non-technical executives
- Outsourcing certain functions to managed service providers (MSPs)
- Optimizing cloud spending to avoid cost overruns
Effective prioritization and ROI analysis are crucial for success in resource-constrained environments.
The Future of the Systems Manager Role
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the role of the systems manager. Emerging trends like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and decentralized networks will reshape responsibilities and expectations.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Automation and AI Integration
AI-driven operations (AIOps) are transforming how systems are monitored and maintained. Machine learning algorithms can predict failures, optimize performance, and even respond to incidents autonomously.
- Reducing manual intervention in routine tasks
- Enhancing decision-making with predictive analytics
- Freeing up time for strategic initiatives
Systems managers will need to become adept at managing AI tools rather than replacing them.
Shift Toward Hybrid and Remote Work Environments
The pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, and many companies now operate in hybrid models. This has increased demand for secure, scalable, and accessible IT systems.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Managing virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI)
- Securing home networks and personal devices
- Ensuring seamless collaboration through cloud-based tools
Systems managers must design architectures that support flexibility without compromising security.
Increased Focus on Sustainability and Green IT
Organizations are becoming more environmentally conscious, and IT departments are under pressure to reduce energy consumption.
- Optimizing data center cooling and power usage
- Migrating to energy-efficient cloud providers
- Implementing server virtualization to reduce physical hardware
The systems manager of the future will need to balance performance with sustainability goals.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What does a systems manager do?
A systems manager oversees the design, implementation, and maintenance of an organization’s IT infrastructure. They ensure systems are secure, efficient, and aligned with business goals, often leading technical teams and managing budgets.
How much does a systems manager earn?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for computer and information systems managers was $164,600 in May 2023. Salaries vary by industry, location, and experience level.
Is a systems manager the same as an IT manager?
Not exactly. While both roles involve IT leadership, a systems manager focuses more on technical infrastructure (servers, networks, operating systems), whereas an IT manager has broader responsibilities including staffing, budgeting, and user support.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What certifications are best for a systems manager?
Top certifications include CISSP for security, AWS Certified Solutions Architect for cloud expertise, and ITIL for service management. CompTIA and Microsoft certifications are also highly valued.
What is the career outlook for systems managers?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The job outlook is excellent, with a projected 16% growth from 2022 to 2032. Demand is driven by increasing reliance on IT systems, cybersecurity needs, and digital transformation initiatives.
The role of a systems manager is more vital than ever in our interconnected world. From securing critical data to enabling digital innovation, these professionals are the backbone of modern organizations. As technology evolves, so too must the skills and strategies of systems managers. By embracing continuous learning, leveraging cutting-edge tools, and aligning IT with business goals, they can drive efficiency, resilience, and growth. Whether you’re aspiring to become one or looking to hire a skilled professional, understanding the depth and breadth of this role is essential for success in the digital age.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: