System Development: 7 Ultimate Power Strategies Revealed
System development isn’t just about coding—it’s the backbone of modern innovation. From healthcare to finance, robust systems power our digital world. Let’s dive into the ultimate strategies that make system development efficient, scalable, and future-proof.
What Is System Development and Why It Matters

System development refers to the structured process of creating, designing, deploying, and maintaining software systems that meet specific user or business needs. It’s more than just writing code; it’s a lifecycle that involves planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. In today’s digital-first world, system development drives automation, efficiency, and innovation across industries.
Defining System Development in Modern Context
Modern system development goes beyond traditional software creation. It includes cloud-based platforms, AI-integrated applications, IoT ecosystems, and mobile-first designs. According to the IEEE Computer Society, system development now encompasses full-stack engineering, DevOps integration, and continuous delivery pipelines.
- Involves interdisciplinary collaboration between developers, analysts, and stakeholders
- Applies engineering principles to software creation
- Focuses on scalability, security, and user experience
Core Objectives of System Development
The primary goal of system development is to deliver functional, reliable, and maintainable software solutions. This involves aligning technical capabilities with business objectives. Whether building an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system or a customer-facing app, the process must ensure that the final product meets user expectations and performs efficiently under real-world conditions.
“System development is not just about building software—it’s about solving real problems with technology.” — Dr. Margaret Burnett, Human-Centered Software Engineering Researcher
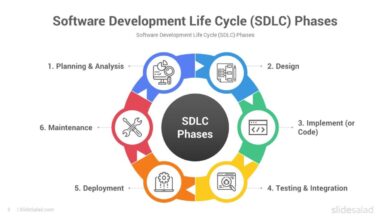
The 7 Phases of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a proven framework used to design, develop, and test high-quality software. It provides a structured approach that minimizes risks and ensures project success. Each phase builds upon the previous one, creating a clear roadmap from concept to deployment.
1. Planning and Requirement Analysis
This initial phase sets the foundation for the entire project. Stakeholders, business analysts, and project managers collaborate to define the scope, objectives, and feasibility of the system. Requirements are gathered through interviews, surveys, and workshops to understand what the system should do.
- Identify user needs and business goals
- Conduct feasibility studies (technical, economic, operational)
- Create a project plan with timelines and resource allocation
Tools like Lucidchart help visualize workflows and data flows during this stage.
2. System Design
Once requirements are clear, the design phase begins. This involves creating architectural blueprints for the system, including data models, interface designs, and system workflows. Designers and architects decide on technology stacks, databases, APIs, and security protocols.
- Develop high-level and low-level design documents
- Choose between monolithic or microservices architecture
- Define UI/UX wireframes and prototypes
A well-documented design reduces development time and prevents costly rework later.
3. Implementation (Coding)
This is where developers write the actual code based on the design specifications. Programming languages, frameworks, and development environments are selected according to the system’s requirements. Agile teams often work in sprints, delivering incremental features.
- Frontend and backend development run in parallel
- Version control systems like Git are used for collaboration
- Code reviews ensure quality and consistency
Platforms like GitHub facilitate collaborative coding and continuous integration.
4. Testing
No system is ready for deployment without rigorous testing. This phase identifies bugs, performance issues, and security vulnerabilities. Different types of testing—unit, integration, system, and user acceptance—are conducted to ensure reliability.
- Automated testing tools like Selenium and JUnit improve efficiency
- Performance testing checks load handling and response times
- Security testing identifies potential exploits
“Testing is not a phase—it’s a mindset.” — Lisa Crispin, Agile Testing Pioneer
5. Deployment
After successful testing, the system is deployed to the production environment. This can be done gradually (phased rollout), all at once (big bang), or in parallel with the old system. CI/CD pipelines automate deployment to reduce human error.
- Use containerization tools like Docker for consistency
- Leverage orchestration platforms like Kubernetes
- Monitor system behavior post-deployment
Companies like Netflix use canary deployments to test new versions on a small user base before full rollout.
6. Maintenance and Updates
Once live, the system requires ongoing maintenance. This includes fixing bugs, applying security patches, optimizing performance, and adding new features based on user feedback.
- Corrective maintenance addresses unexpected issues
- Adaptive maintenance adjusts to new environments (e.g., OS updates)
- Perfective maintenance enhances functionality
Regular updates keep the system secure and relevant in a fast-changing tech landscape.
7. Evaluation and Feedback Loop
The final phase involves assessing the system’s performance against initial goals. User feedback, analytics, and system logs are analyzed to identify areas for improvement. This phase closes the loop and often triggers a new development cycle.
- Conduct post-implementation reviews
- Measure KPIs like uptime, response time, and user satisfaction
- Document lessons learned for future projects
This continuous evaluation ensures long-term success and adaptability.
Popular System Development Methodologies Compared
Different projects require different approaches. Choosing the right methodology impacts project speed, flexibility, and success rate. Let’s explore the most widely used models in system development today.
Waterfall Model: The Traditional Approach
The Waterfall model follows a linear, sequential approach where each phase must be completed before the next begins. It’s ideal for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal expected changes.
- Simple to understand and manage
- Clear documentation at each stage
- Poor flexibility for changes once development starts
Best suited for government or regulated industries where compliance and documentation are critical.
Agile Methodology: Flexibility and Speed
Agile is the most popular methodology in modern system development. It emphasizes iterative development, customer collaboration, and rapid delivery. Teams work in short cycles (sprints) to deliver functional increments of the system.
- High adaptability to changing requirements
- Frequent feedback from stakeholders
- Requires strong team coordination and communication
According to the State of Agile Report, over 90% of organizations use Agile in some form.
“Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.” — Agile Manifesto Principle
DevOps: Bridging Development and Operations
DevOps is not just a methodology—it’s a cultural shift that integrates development and IT operations. It enables faster delivery, improved collaboration, and automated deployment pipelines.
- Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are core practices
- Monitoring and logging are built into the system
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) ensures consistency
Tools like Jenkins, Ansible, and Terraform are essential in DevOps-driven system development.
Key Technologies Powering Modern System Development
Technology evolves rapidly, and system development must keep pace. Today’s developers leverage a wide array of tools and platforms to build scalable, secure, and intelligent systems.
Cloud Computing and System Development
Cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have revolutionized system development. They offer on-demand computing resources, reducing infrastructure costs and enabling global scalability.
- Serverless computing allows developers to focus on code, not servers
- Cloud-native applications are designed for elasticity and resilience
- Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies provide flexibility
As noted by Amazon Web Services, cloud adoption accelerates time-to-market by up to 50%.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI and ML are no longer futuristic concepts—they’re integral to modern system development. From chatbots to predictive analytics, intelligent systems enhance user experience and automate decision-making.
- AI-powered testing tools detect bugs faster
- ML models personalize user experiences in real time
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) improves system interactivity
Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch are widely used in AI-driven system development.
Microservices and Containerization
Monolithic architectures are giving way to microservices—small, independent services that communicate via APIs. This approach improves scalability, fault isolation, and deployment speed.
- Each service can be developed, tested, and deployed independently
- Containers (Docker) package applications with their dependencies
- Kubernetes manages container orchestration at scale
Companies like Uber and Spotify rely on microservices to handle millions of users daily.
Best Practices for Successful System Development
Even with the right tools and methodologies, system development can fail without proper practices. Here are proven strategies to ensure project success.
Start with Clear Requirements
Vague or incomplete requirements are the top cause of project failure. Use techniques like user stories, use cases, and requirement traceability matrices to capture and validate needs early.
- Engage stakeholders from day one
- Prioritize requirements using MoSCoW (Must, Should, Could, Won’t)
- Document everything to avoid scope creep
As the Project Management Institute (PMI) states, projects with well-defined requirements are 2.5x more likely to succeed.
Embrace Version Control
Version control is non-negotiable in system development. It tracks changes, enables collaboration, and provides a safety net for rollbacks.
- Use Git for distributed version control
- Adopt branching strategies like GitFlow
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines
Without version control, teams risk losing code, overwriting work, and lacking audit trails.
Implement Continuous Testing
Testing shouldn’t be an afterthought. Integrate automated testing throughout the development cycle to catch issues early.
- Write unit tests for every function
- Use test-driven development (TDD) for higher code quality
- Run integration and performance tests regularly
“The earlier you catch a bug, the cheaper it is to fix.” — Steve McConnell, Author of ‘Code Complete’
Common Challenges in System Development and How to Overcome Them
Despite best efforts, system development projects face numerous challenges. Recognizing these early allows teams to mitigate risks effectively.
Scope Creep and Changing Requirements
One of the biggest threats to project timelines is scope creep—uncontrolled changes or additions to the project scope. This often stems from unclear initial requirements or stakeholder pressure.
- Solution: Use change control boards to evaluate and approve new requests
- Solution: Adopt Agile to accommodate changes in a structured way
- Solution: Maintain a prioritized backlog
According to the Project Management Institute, 52% of failed IT projects cite poor requirement management as a key factor.
Communication Gaps Between Teams
Miscommunication between developers, testers, and business stakeholders can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and incorrect implementations.
- Solution: Hold daily stand-ups and regular sprint reviews
- Solution: Use collaboration tools like Slack, Jira, and Confluence
- Solution: Create shared documentation accessible to all
Effective communication reduces rework and aligns everyone with project goals.
Security Vulnerabilities
With rising cyber threats, security can’t be an afterthought. Many systems are compromised due to poor coding practices or outdated dependencies.
- Solution: Integrate security testing (penetration testing, code scanning)
- Solution: Follow secure coding guidelines (OWASP Top 10)
- Solution: Regularly update libraries and frameworks
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) provides free resources to help developers build secure systems.
The Future of System Development: Trends to Watch
System development is evolving at a rapid pace. Emerging technologies and methodologies are reshaping how we build software.
No-Code and Low-Code Platforms
These platforms allow non-developers to create applications using drag-and-drop interfaces. While not suitable for complex systems, they accelerate prototyping and internal tool development.
- Tools like Microsoft Power Apps and Bubble are gaining traction
- Reduce dependency on IT departments for simple apps
- Enable citizen developers to contribute
Gartner predicts that by 2025, 70% of new applications will use low-code/no-code technologies.
AI-Powered Development Tools
AI is now assisting developers with code generation, bug detection, and optimization. Tools like GitHub Copilot suggest code snippets in real time, boosting productivity.
- AI reduces repetitive coding tasks
- Automated code reviews improve quality
- Predictive analytics help estimate project timelines
These tools don’t replace developers—they augment their capabilities.
Sustainable and Green Software Engineering
As environmental concerns grow, the tech industry is focusing on energy-efficient coding. Green software engineering aims to reduce the carbon footprint of digital systems.
- Optimize algorithms for lower energy consumption
- Use energy-aware cloud services
- Design for longevity and minimal resource usage
Organizations like the Green Software Foundation are leading this movement.
What is the most important phase in system development?
The most critical phase is requirement analysis. Without clear, accurate, and complete requirements, even the best-designed system can fail to meet user needs. This phase sets the direction for the entire project and influences every subsequent step.
What’s the difference between SDLC and Agile?
SDLC (System Development Life Cycle) is a broad framework that describes the stages of system development. Agile is a specific methodology within SDLC that emphasizes iterative development, collaboration, and flexibility. While SDLC can follow linear models like Waterfall, Agile promotes continuous delivery and adaptation.
How long does system development typically take?
Duration varies widely based on project complexity. A simple web application might take 3–6 months, while large enterprise systems can take 1–3 years. Agile projects often deliver value in weeks or months through incremental releases.
Is coding the most important part of system development?
No—while coding is essential, it’s only one phase. Planning, design, testing, and maintenance are equally crucial. A well-planned system with poor code can fail, just as brilliant code with poor requirements will miss the mark.
What skills are needed for system development?
Key skills include programming, system analysis, database design, project management, and problem-solving. Soft skills like communication, teamwork, and adaptability are also vital, especially in Agile and DevOps environments.
System development is a dynamic, multifaceted discipline that powers the digital world. From defining requirements to deploying intelligent systems, every phase plays a crucial role in delivering value. By understanding the SDLC, choosing the right methodology, leveraging modern technologies, and following best practices, teams can build systems that are not only functional but also scalable, secure, and future-ready. As AI, cloud computing, and sustainable engineering shape the future, staying informed and adaptable is key to success in this ever-evolving field.
Further Reading: