System Design Interview: 7 Ultimate Secrets to Dominate
Navigating a system design interview can feel like preparing for a marathon blindfolded. But what if you had a proven roadmap? This guide reveals the ultimate strategies to not just survive, but dominate your next system design interview with confidence and clarity.
What Is a System Design Interview?

A system design interview is a critical component of the technical hiring process, especially at top-tier tech companies like Google, Amazon, and Meta. Unlike coding interviews that test algorithmic thinking, system design interviews assess your ability to design scalable, reliable, and maintainable systems from scratch.
Core Objectives of the Interview
The primary goal is to evaluate how well you can break down complex problems, make trade-offs, and communicate your thought process. Interviewers aren’t looking for a single correct answer—they want to see structured thinking, awareness of system constraints, and the ability to iterate on design choices.
- Assess problem-solving and architectural skills
- Evaluate communication and collaboration abilities
- Test knowledge of distributed systems, databases, and networking
Common Formats and Variants
System design interviews can vary in scope and depth. Some are high-level, asking you to design a URL shortener or a chat application, while others dive deep into specific subsystems like caching layers or database sharding.
- High-Level Design (HLD): Focuses on overall architecture, components, and data flow.
- Low-Level Design (LLD): Delves into class structures, APIs, and implementation details.
- Hybrid Interviews: Combine both HLD and LLD, often starting broad and narrowing down.
“The best candidates don’t just design systems—they explain why they made each decision.” — Engineering Manager, Google
Why System Design Interviews Matter
As software systems grow in complexity, companies need engineers who can think beyond writing code. A system design interview separates those who can build small features from those who can architect entire platforms.
Role in Tech Hiring at FAANG Companies
At FAANG (Facebook/Meta, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, Google) and similar tech giants, system design interviews are often the final gatekeeper before an offer. These companies operate at massive scale, so they need engineers who understand how to design systems that handle millions of users and petabytes of data.
- Used to assess seniority level (L4 and above at Google)
- Often weighted more heavily than coding rounds for mid-to-senior roles
- Helps identify candidates who can lead technical projects
Impact on Career Growth and Promotions
Strong system design skills aren’t just useful for landing a job—they’re essential for career advancement. Engineers who can design robust systems are more likely to be promoted to senior, staff, or principal levels.
- Senior engineers are expected to own system architecture
- Promotions often require demonstrating design leadership
- Design skills translate into better technical decision-making
Core Concepts Every Candidate Must Know
Before diving into design patterns, you need a solid grasp of foundational concepts. These are the building blocks of any scalable system and are frequently tested in a system design interview.
Scalability: Vertical vs. Horizontal
Scalability refers to a system’s ability to handle increased load. There are two main approaches:
- Vertical Scaling: Adding more power (CPU, RAM) to a single server. Simple but has limits.
- Horizontal Scaling: Adding more servers to distribute the load. More complex but essential for large-scale systems.
Most modern systems rely on horizontal scaling, often using load balancers to distribute traffic. For example, AWS Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets.
Availability and Reliability
Availability is the percentage of time a system is operational. Reliability refers to the system’s ability to perform consistently under stress.
- High availability often targets “five nines” (99.999%) uptime
- Techniques include redundancy, failover mechanisms, and health checks
- Reliability is improved through monitoring, logging, and automated recovery
“Design for failure. Assume everything will break, and build accordingly.” — Werner Vogels, CTO of Amazon
Latency, Throughput, and Consistency
These are key performance metrics in system design:
- Latency: Time taken for a request to travel from client to server and back.
- Throughput: Number of requests a system can handle per second.
- Consistency: Ensures all nodes see the same data at the same time (challenging in distributed systems).
Understanding the CAP theorem (Consistency, Availability, Partition Tolerance) is crucial. You can only guarantee two out of three in a distributed system. Learn more at InfoQ’s guide on NoSQL consistency.
Step-by-Step Framework for Tackling Any System Design Interview
Having a repeatable framework is the single biggest advantage you can have. Follow this proven 6-step process to structure your response and impress interviewers.
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Step 1: Clarify Requirements
Never jump into design without understanding the problem. Ask clarifying questions to define functional and non-functional requirements.
- Who are the users? (e.g., 1M daily active users)
- What are the core features? (e.g., post, like, comment)
- What are the performance goals? (e.g., 100ms latency)
- Is it read-heavy or write-heavy?
Example: For a Twitter-like system, ask if retweets are included, whether images are supported, and expected growth rate.
Step 2: Estimate Scale
Back-of-the-envelope calculations show you think quantitatively. Estimate traffic, storage, and bandwidth needs.
- Requests per second (QPS): 1M DAU × 10 reads/user/day ≈ 115 QPS
- Storage: 1M users × 1KB/user × 365 days ≈ 365GB/year
- Bandwidth: 115 QPS × 1KB = ~115 KB/s
These numbers guide your architecture decisions—e.g., whether you need caching or database sharding.
Step 3: Define System Interface
Sketch the API contracts. What endpoints will the system expose?
- GET /post/{id} → returns post details
- POST /post → creates a new post
- GET /feed → returns user’s timeline
This step sets the stage for component design and helps align your thinking with real-world integration.
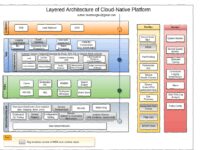
Step 4: High-Level Architecture
Draw a block diagram showing major components: clients, load balancers, web servers, databases, caches, message queues, etc.
- Use a three-tier architecture: Presentation, Application, Data
- Identify stateless vs. stateful services
- Show data flow between components
For example, in a video streaming service, you might have CDN for video delivery, a metadata database, and a recommendation engine.
Step 5: Deep Dive into Key Components
Now, zoom in on critical parts. How will the database be structured? Should you use SQL or NoSQL?
- For user data: SQL (strong consistency)
- For activity feeds: NoSQL (high write throughput)
- Consider denormalization for performance
Discuss indexing strategies, sharding keys (e.g., user ID), and replication models (master-slave vs. multi-master).
Step 6: Identify and Solve Bottlenecks
Every design has weaknesses. Proactively identify them and propose solutions.
- Bottleneck: Database overload from read traffic → Solution: Add Redis cache
- Bottleneck: Slow feed generation → Solution: Pre-compute timelines
- Bottleneck: Single point of failure → Solution: Add redundancy and failover
This shows foresight and engineering maturity—exactly what interviewers want.
Common System Design Interview Questions and How to Approach Them
Certain problems appear so frequently they’ve become classics. Mastering these gives you a huge edge in any system design interview.
Design a URL Shortener (e.g., TinyURL)
This tests your ability to handle ID generation, redirection, and scalability.
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Use hash functions (e.g., MD5) or base-62 encoding of auto-increment IDs
- Store mappings in a distributed key-value store like DynamoDB
- Cache hot URLs in Redis for low-latency redirects
- Handle expiration and cleanup with TTL or background jobs
Learn how Bitly handles scale at Bitly Engineering Blog.
Design a Chat Application (e.g., WhatsApp)
This is a complex problem involving real-time communication, message delivery guarantees, and offline support.
- Use WebSockets or MQTT for real-time messaging
- Store messages in a durable message queue like Kafka
- Implement message syncing across devices using vector clocks or CRDTs
- Ensure end-to-end encryption for privacy
Consider trade-offs: persistent connections vs. battery life, read receipts, and group chat scaling.
Design a Distributed Cache
Caching is critical for performance. This question tests your knowledge of eviction policies, consistency, and distribution.
- Choose eviction policies: LRU, LFU, or TTL-based
- Use consistent hashing to distribute keys across nodes
- Handle cache invalidation: write-through, write-behind, or cache-aside
- Consider cache coherence in multi-writer scenarios
Redis and Memcached are real-world examples. Study Redis’s distributed locking for advanced patterns.
Advanced Topics That Can Make or Break Your System Design Interview
Once you’ve mastered the basics, diving into advanced topics can set you apart. These are often the differentiators between a good and a great candidate.
Database Sharding and Replication
Sharding splits a database into smaller, manageable pieces. Replication ensures data redundancy and availability.
- Sharding Strategies: Range-based, hash-based, or directory-based
- Sharding Key: Choose wisely (e.g., user ID vs. geographic region)
- Replication Models: Master-slave (asynchronous/synchronous), multi-master
- Challenges: Rebalancing shards, cross-shard queries, and transaction support
For example, Instagram shards user data by user ID using a consistent hashing ring.
Message Queues and Event-Driven Architecture
Asynchronous processing is key to decoupling services and improving scalability.
- Use message queues like Kafka, RabbitMQ, or AWS SQS
- Implement event sourcing for audit trails and state reconstruction
- Handle message ordering, deduplication, and retries
- Design for eventual consistency in distributed workflows
Netflix uses Kafka extensively for real-time analytics and service communication. Read more at Netflix Tech Blog.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and Edge Computing
CDNs reduce latency by serving content from locations closer to users.
- Cache static assets (images, videos, JS files) at edge locations
- Use geolocation to route users to nearest POP (Point of Presence)
- Implement cache invalidation strategies (push vs. pull)
- Edge computing allows running logic at the edge (e.g., AWS Lambda@Edge)
Cloudflare and Akamai are leaders in this space. Explore Cloudflare’s CDN guide for deeper insights.
How to Prepare for a System Design Interview: A 30-Day Plan
Preparation is everything. A structured 30-day plan can transform your readiness and confidence for the system design interview.
Week 1: Master the Fundamentals
Build a strong foundation in distributed systems concepts.
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Study scalability, availability, CAP theorem, and consistency models
- Read Donne Martin’s System Design Primer (free and comprehensive)
- Watch lectures from MIT’s Distributed Systems course
Week 2: Practice Common Problems
Apply theory to real interview questions.
- Solve 3-5 system design problems (e.g., design Twitter, Dropbox, Uber)
- Use the 6-step framework consistently
- Record yourself explaining the design to improve communication
Week 3: Deep Dive into Advanced Topics
Go beyond the basics.
- Study database internals, consensus algorithms (Paxos, Raft)
- Explore microservices, service mesh, and observability
- Read papers like Google’s Bigtable and Amazon’s Dynamo
Week 4: Mock Interviews and Feedback
Simulate real conditions.
- Conduct 3-5 mock interviews with peers or mentors
- Use platforms like Pramp or Interviewing.io for realistic practice
- Refine based on feedback: clarity, depth, and structure
What are the key skills tested in a system design interview?
The key skills include architectural thinking, scalability planning, trade-off analysis, communication, and problem decomposition. Interviewers also assess your knowledge of databases, caching, networking, and distributed systems.
How long should I prepare for a system design interview?
Most candidates need 4–8 weeks of focused preparation. Beginners should allocate more time to grasp fundamentals, while experienced engineers can focus on refining communication and practicing complex scenarios.
Is coding required in a system design interview?
Typically, no extensive coding is required. However, you may need to write pseudocode for critical algorithms (e.g., consistent hashing) or sketch API endpoints. The focus is on design, not implementation.
What tools can I use to practice system design?
Popular resources include the System Design Primer, books like “Designing Data-Intensive Applications” by Martin Kleppmann, and platforms like Pramp and Interviewing.io for mock interviews.
How do I handle unfamiliar system design questions?
Stick to the framework: clarify, estimate, define API, sketch architecture, dive deep, and address bottlenecks. Even if you don’t know the domain, structured thinking will impress interviewers.
Mastering the system design interview is not about memorizing answers—it’s about developing a mindset. By understanding core principles, practicing with a structured approach, and learning from real-world systems, you can confidently tackle any design challenge. Whether you’re aiming for a role at a tech giant or building your own startup, these skills are invaluable. Start early, practice consistently, and remember: every great system begins with a single, well-thought-out design.
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: