System Backup: 7 Ultimate Strategies for Total Data Protection
Imagine losing every document, photo, and critical file in an instant. That’s the reality without a solid system backup strategy. In today’s digital world, data is everything—your business, memories, and operations depend on it. Let’s explore how to protect it all.
What Is a System Backup and Why It Matters

A system backup is the process of copying and archiving computer data so it can be restored after a data loss event. Whether due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, or human error, having a reliable system backup ensures continuity and peace of mind.
Defining System Backup
At its core, a system backup involves creating a duplicate of your operating system, applications, settings, and files. Unlike file-level backups, which only copy individual documents, a full system backup captures the entire state of your machine. This allows for complete restoration to a previous point in time.
- Includes OS, installed programs, configurations, and user data
- Enables full system recovery after crashes or malware attacks
- Can be performed locally, in the cloud, or via hybrid models
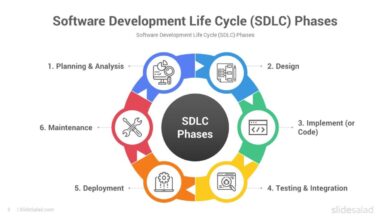
Types of System Backup
There are three primary types of system backup: full, incremental, and differential. Each has its own advantages and use cases.
- Full Backup: Copies all data every time. Most secure but resource-intensive.
- Incremental Backup: Only saves changes since the last backup (any type). Fast and efficient but slower to restore.
- Differential Backup: Saves changes since the last full backup. Balances speed and restore efficiency.
“A backup is only as good as its ability to be restored.” — Unknown
The Critical Importance of System Backup
Data loss isn’t a matter of if, but when. From ransomware to accidental deletions, threats are everywhere. A robust system backup strategy is your last line of defense.
Protecting Against Cyber Threats
Ransomware attacks have surged in recent years, with attackers encrypting data and demanding payment for decryption. According to CISA, over 2,300 organizations were impacted by ransomware in 2023 alone. A proper system backup allows you to restore your data without paying the ransom.
- Backups act as a recovery point after malware infection
- Isolated or offline backups prevent attackers from encrypting backup files
- Regular testing ensures backups are usable when needed
Preventing Data Loss from Hardware Failure
Hard drives fail. SSDs wear out. According to a Backblaze study, the average annual hard drive failure rate is around 1.6%. For businesses, this can mean catastrophic data loss. A system backup ensures that even if your hardware dies, your data lives on.
- RAID is not a backup—redundancy doesn’t protect against deletion or corruption
- System backups allow migration to new hardware seamlessly
- Cloud-based backups offer geographic redundancy
Top 7 System Backup Strategies You Must Know
Not all backups are created equal. To ensure maximum protection, you need a strategic approach. Here are seven proven system backup strategies that professionals use to safeguard their data.
1. The 3-2-1 Backup Rule
This is the gold standard in data protection. The 3-2-1 rule states: keep three copies of your data, on two different media, with one copy offsite.
- Three copies: Original + two backups
- Two media types: e.g., external drive + cloud storage
- One offsite: Protects against physical disasters like fire or theft
This strategy minimizes risk and ensures redundancy. For example, you might keep your primary data on your laptop, a backup on an external SSD, and another in Google Drive or AWS Backup.
2. Automate Your System Backup
Manual backups are unreliable. People forget. Automation ensures consistency and reduces human error.
- Use built-in tools like Windows Backup and Restore or macOS Time Machine
- Leverage third-party software like Acronis True Image or Veeam
- Schedule backups during off-peak hours to minimize performance impact
Automation also allows for versioning—keeping multiple restore points over time. This is crucial for recovering from undetected corruption or malware that spreads silently.
3. Use Versioned Backups
Versioning means keeping multiple historical copies of your files. This protects against accidental overwrites, ransomware, and data corruption.
- Cloud services like Dropbox and OneDrive offer file versioning
- Backup tools like Duplicati and BorgBackup support incremental versioning
- Retain versions for at least 30 days (longer for critical data)
For example, if a file is encrypted by ransomware today, you can restore it from a clean version from yesterday.
4. Implement Offsite and Cloud Backups
Local backups are vulnerable to physical threats. Offsite backups—especially in the cloud—add a critical layer of protection.
- Cloud providers like Google Drive, Dropbox, and Microsoft Azure offer scalable, secure storage
- Encryption ensures data privacy even in the cloud
- Geographic redundancy protects against regional disasters
Hybrid models—combining local and cloud backups—are ideal for balancing speed and security.
5. Test Your System Backup Regularly
Many organizations assume their backups work—until they don’t. Testing is essential to verify integrity and usability.
- Perform test restores quarterly (or monthly for critical systems)
- Check file integrity, bootability (for system images), and data consistency
- Document results and update procedures as needed
According to a Veritas study, 14% of businesses discovered their backups were unusable during a crisis. Don’t be one of them.
6. Encrypt Your Backups
Backups contain sensitive data. If stolen or exposed, they can lead to data breaches.
- Use AES-256 encryption for both local and cloud backups
- Store encryption keys separately from backup media
- Enable two-factor authentication for cloud backup accounts
Tools like VeraCrypt and BitLocker can secure external drives, while most cloud services offer built-in encryption options.
7. Adopt a Tiered Backup Approach
Not all data is equally important. A tiered strategy prioritizes backups based on criticality and recovery needs.
- Tier 1: Mission-critical data (e.g., databases, financial records) – backed up hourly, stored offsite
- Tier 2: Important but not urgent (e.g., project files) – daily backups
- Tier 3: Archival or low-priority data – weekly or monthly backups
This optimizes storage costs and recovery time objectives (RTO).
Best Tools for System Backup in 2024
Choosing the right tool is crucial for an effective system backup strategy. Here’s a breakdown of the top solutions available today.
Windows Built-in Tools
Windows offers several native backup options that are free and easy to use.
- File History: Backs up personal files to an external drive or network location
- Backup and Restore (Windows 7): Allows full system image backups
- System Image Backup: Creates a complete snapshot of your drive
While limited in features, these tools are sufficient for basic home users.
macOS Time Machine
Apple’s Time Machine is one of the most user-friendly system backup solutions.
- Automatically backs up your entire system to an external drive
- Supports versioning with hourly, daily, and weekly snapshots
- Easy restoration via bootable recovery mode
For Mac users, Time Machine is a must-have. Pair it with a cloud service for offsite protection.
Third-Party Backup Software
For advanced features and cross-platform support, third-party tools are ideal.
- Acronis True Image: Offers full disk imaging, cloud backup, and ransomware protection
- Macrium Reflect: Popular for Windows, supports imaging and cloning
- Veeam Backup & Replication: Enterprise-grade solution for virtual and physical environments
- Duplicati: Open-source, encrypted, cloud-compatible backup tool
These tools often include scheduling, compression, encryption, and remote management.
Cloud-Based System Backup Solutions
Cloud backups have revolutionized data protection by offering scalability, accessibility, and automation.
Advantages of Cloud Backup
Cloud-based system backup eliminates the need for physical media and provides several key benefits.
- Automatic syncing: Files are backed up in real-time or on schedule
- Access from anywhere: Recover data from any device with internet access
- Scalable storage: Pay only for what you use, with options to expand
- Disaster recovery: Offsite storage protects against physical damage
Services like IDrive and CrashPlan specialize in full system backups to the cloud.
Security Considerations for Cloud Backup
While convenient, cloud backups raise security concerns. Here’s how to stay safe.
- Choose providers with end-to-end encryption (zero-knowledge architecture)
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication
- Review privacy policies and data jurisdiction laws
- Avoid storing unencrypted sensitive data (e.g., passwords, financial records)
Remember: the cloud is only as secure as your access controls.
Common System Backup Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, many people make critical errors in their backup strategy.
Assuming Backups Are Working Without Testing
One of the most dangerous assumptions is that “it’s backing up, so it must work.” Without testing, you won’t know until it’s too late.
- Corrupted backups can’t be restored
- Software bugs or configuration errors may prevent proper backup
- Regular test restores are non-negotiable
Storing Backups on the Same Device
Keeping backups on the same hard drive or connected external drive is risky. If the device fails or gets infected, both original and backup data are lost.
- Always disconnect external drives after backup (or use immutable storage)
- Use network-attached storage (NAS) or cloud for separation
- Consider air-gapped backups for high-security environments
Ignoring Backup Retention Policies
How long should you keep backups? Too short, and you lose recovery options. Too long, and you waste resources.
- Define retention periods based on data importance
- Use automated cleanup to remove outdated backups
- Comply with legal or industry requirements (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR)
How to Create a System Backup Plan for Your Business
For organizations, a formal backup plan is essential for compliance, continuity, and risk management.
Assess Your Data and Recovery Needs
Start by identifying what data you have, where it’s stored, and how critical it is.
- Classify data by sensitivity and importance
- Determine Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
- Map data flows and storage locations
This assessment forms the foundation of your backup strategy.
Choose the Right Backup Infrastructure
Decide between on-premises, cloud, or hybrid solutions based on budget, security, and performance needs.
- On-premises: Full control, but higher upfront cost
- Cloud: Lower cost, scalable, but dependent on internet
- Hybrid: Best of both worlds, but more complex to manage
For example, a small business might use a NAS with cloud sync, while an enterprise might deploy Veeam with AWS integration.
Document and Train Your Team
A backup plan is only effective if everyone understands it.
- Create a written backup policy with roles and responsibilities
- Train staff on backup procedures and incident response
- Conduct regular drills to simulate data loss scenarios
Documentation ensures continuity during staff changes or emergencies.
Future Trends in System Backup Technology
The world of data protection is evolving rapidly. Here’s what’s on the horizon.
AI-Powered Backup and Recovery
Artificial intelligence is being used to detect anomalies, predict failures, and automate recovery.
- AI can identify unusual file access patterns (potential ransomware)
- Predictive analytics can warn of impending drive failure
- Automated recovery workflows reduce downtime
Companies like Rubrik and Cohesity are already integrating AI into their platforms.
Immutable Backups and Cyber Resilience
Immutable backups cannot be altered or deleted for a set period, making them immune to ransomware.
- Object lock features in cloud storage (e.g., S3 Object Lock)
- Write-once-read-many (WORM) storage for compliance
- Part of a broader cyber resilience strategy
This is becoming a standard requirement for regulated industries.
Edge Computing and Decentralized Backup
As data moves to the edge (IoT devices, remote offices), backup strategies must adapt.
- Distributed backup networks reduce reliance on central servers
- Blockchain-based storage offers tamper-proof records
- Peer-to-peer backup models are emerging
These trends promise greater resilience and autonomy.
What is the 3-2-1 backup rule?
The 3-2-1 backup rule recommends keeping three copies of your data, on two different storage types, with one copy stored offsite. This strategy minimizes the risk of total data loss due to hardware failure, theft, or natural disasters.
How often should I perform a system backup?
For most users, daily backups are sufficient. Businesses with critical data may need hourly or real-time backups. The frequency should align with your Recovery Point Objective (RPO)—how much data loss you can tolerate.
Is cloud backup safe for system backup?
Yes, cloud backup can be safe if you choose a reputable provider with strong encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications. Always enable two-factor authentication and use client-side encryption for sensitive data.
Can I restore a system backup to a different computer?
Yes, but it depends on the backup method and hardware compatibility. System image backups may require adjustments for different drivers or architectures. Tools like Macrium Reflect and Acronis offer universal restore features.
What’s the difference between backup and sync?
Backup creates a historical copy for recovery, while sync keeps files identical across devices in real-time. Syncing does not protect against deletion or corruption—deleted files are often synced for deletion. Always use backup for protection.
System backup is not a luxury—it’s a necessity. From personal photos to enterprise databases, every bit of data deserves protection. By following the 3-2-1 rule, automating backups, testing regularly, and embracing cloud and encryption technologies, you can build a resilient data protection strategy. The cost of backup is minimal compared to the cost of data loss. Start today, stay protected tomorrow.
Further Reading: